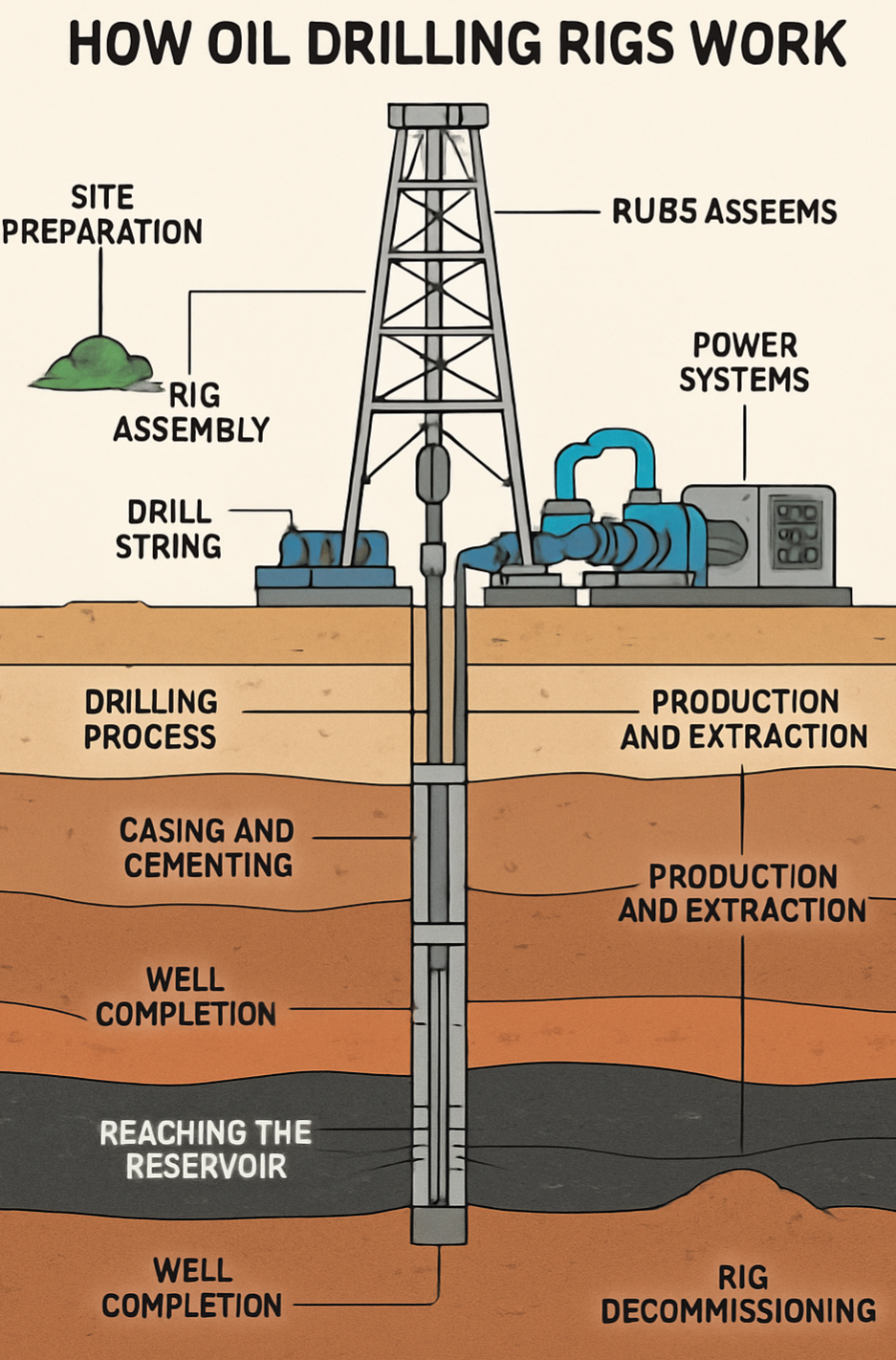
How Oil Drilling Rigs Work
Oil drilling rigs are complex systems designed to extract crude oil from beneath the Earth's surface. They can be located on land (onshore rigs) or at sea (offshore rigs). The process of drilling for oil involves several critical stages, supported by advanced engineering and technology.
1. Site Preparation
Before drilling begins, geologists conduct surveys to identify potential oil reserves. Once a site is selected, the area is cleared, and infrastructure is built, including roads, foundations, and storage areas.
2. Rig Assembly
The drilling rig is assembled on-site. Key components include:
Derrick: The tall structure that supports the drill string.
Drill String: A series of connected pipes with a drill bit at the end.
Mud Pumps: Circulate drilling fluid (mud) into the well.
Power Systems: Provide the necessary energy for drilling operations.
3. Drilling Process
Drilling begins with the creation of a surface hole, usually lined with casing to prevent collapse. The drill bit, driven by a rotary table or top drive, grinds through rock layers to reach the oil reservoir. Drilling mud is pumped into the well to:
Cool the drill bit,
Remove rock cuttings,
Maintain pressure and prevent blowouts.
4. Casing and Cementing
As the drill penetrates deeper, steel casings are inserted into the hole to stabilize the well. Cement is pumped around the casing to secure it and isolate different underground layers.
5. Reaching the Reservoir
Once the oil reservoir is reached, a final casing is installed. If tests confirm the presence of oil, the well is prepared for production.
6. Well Completion
Perforations are made in the casing to allow oil to flow into the well. Sometimes, techniques like hydraulic fracturing (fracking) or acidizing are used to enhance flow.
7. Production and Extraction
Oil is pumped to the surface using mechanical or natural pressure. It is then transported via pipelines, trucks, or ships to refineries.
8. Rig Decommissioning
When a well is no longer productive, it is sealed with cement, the equipment is removed, and the land or seafloor is restor
ed as close to its original condition as possible.


You must be logged in to post a comment.